Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia:
Mesopotamia, known as the "Cradle of Civilization," was crucial because it saw the development of some of the earliest human societies and inventions, like writing and the wheel. Its location between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers made it ideal for agriculture, which allowed large populations to thrive and create complex cities like Babylon and Ur. This innovation responded to the need for organized societies and solutions to challenges like flooding and food supply. Today, Mesopotamia's innovations continue to affect our lives, such as the concept of time (with 60-minute hours) and urban planning. For example, when you use a calendar or live in a city with roads and buildings, you're benefiting from ideas that originated in Mesopotamia.

Practice Version
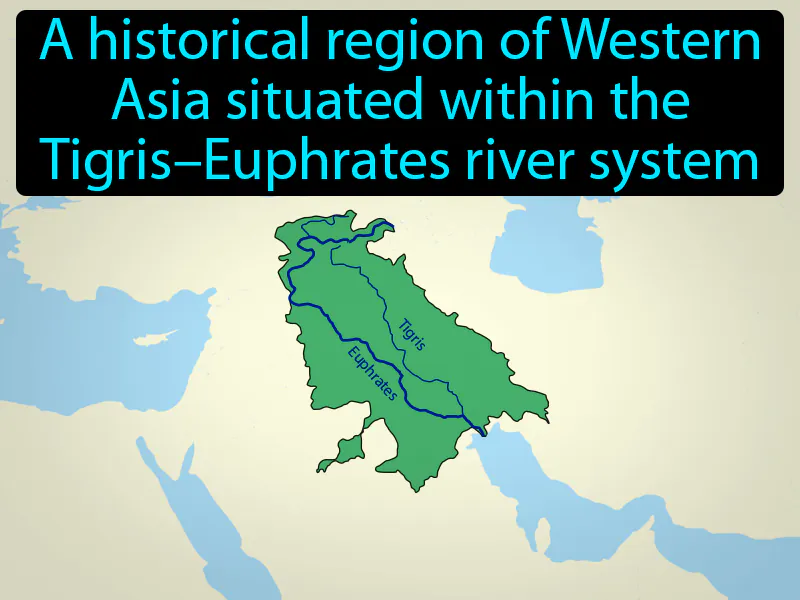
Mesopotamia: A historical region of Western Asia situated within the TigrisEuphrates river system. Mesopotamia. It is often called the "cradle of civilization" because it is where some of the earliest human civilizations began.