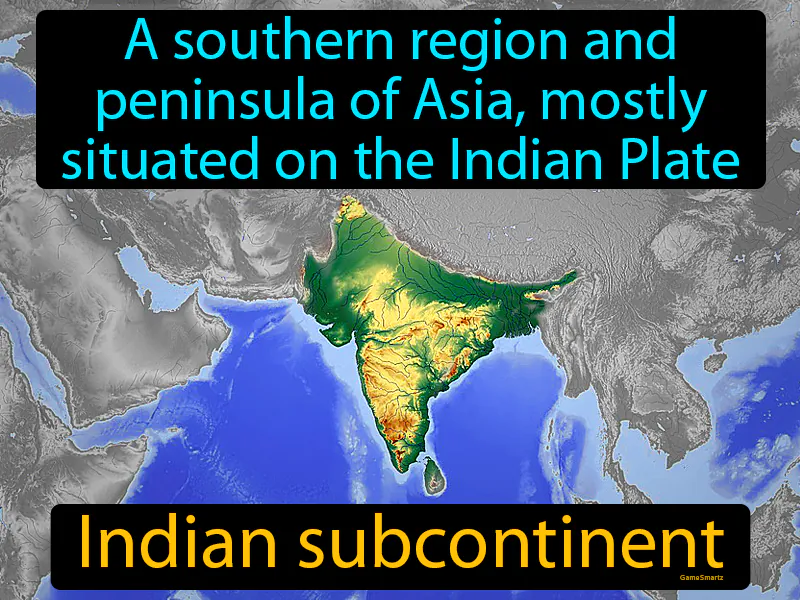
Indian Subcontinent
Indian Subcontinent:
The Indian subcontinent, during ancient times from 2600 BC to 550 AD, was a cradle of early civilizations like the Indus Valley and later, the Maurya and Gupta Empires. It was crucial as a hub for trade, culture, and religion, connecting regions like China through the Silk Road, which facilitated the exchange of goods, ideas, and technologies. This region addressed the need for organized societies and facilitated interactions with neighboring civilizations, impacting cultural and economic growth. Today, the Indian subcontinent remains important due to its vast population, diverse cultures, and significant contributions to global economics and technology. An example of its influence is the widespread popularity of Indian cuisine worldwide, which introduces people to new tastes and fosters cultural appreciation and exchange in everyday life.
Practice Version
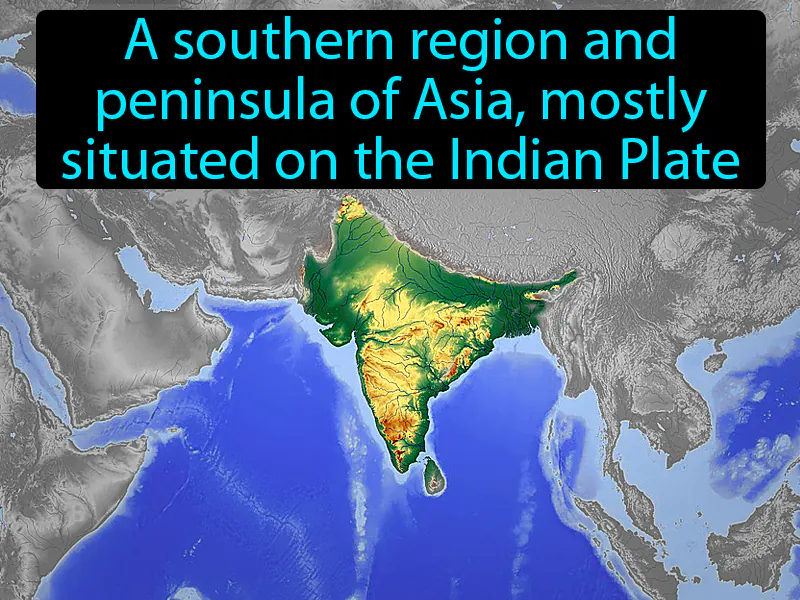
Indian Subcontinent: A southern region and peninsula of Asia, mostly situated on the Indian Plate. Indian subcontinent. The Indian subcontinent is a historical region where ancient civilizations like the Indus Valley thrived.